The <form> Element
The HTML: <form> element is used to create an HTML form for user input:
<form>

</form> The Element The HTML element is the most used form element.
An element can be displayed in many ways, depending on the type attribute.
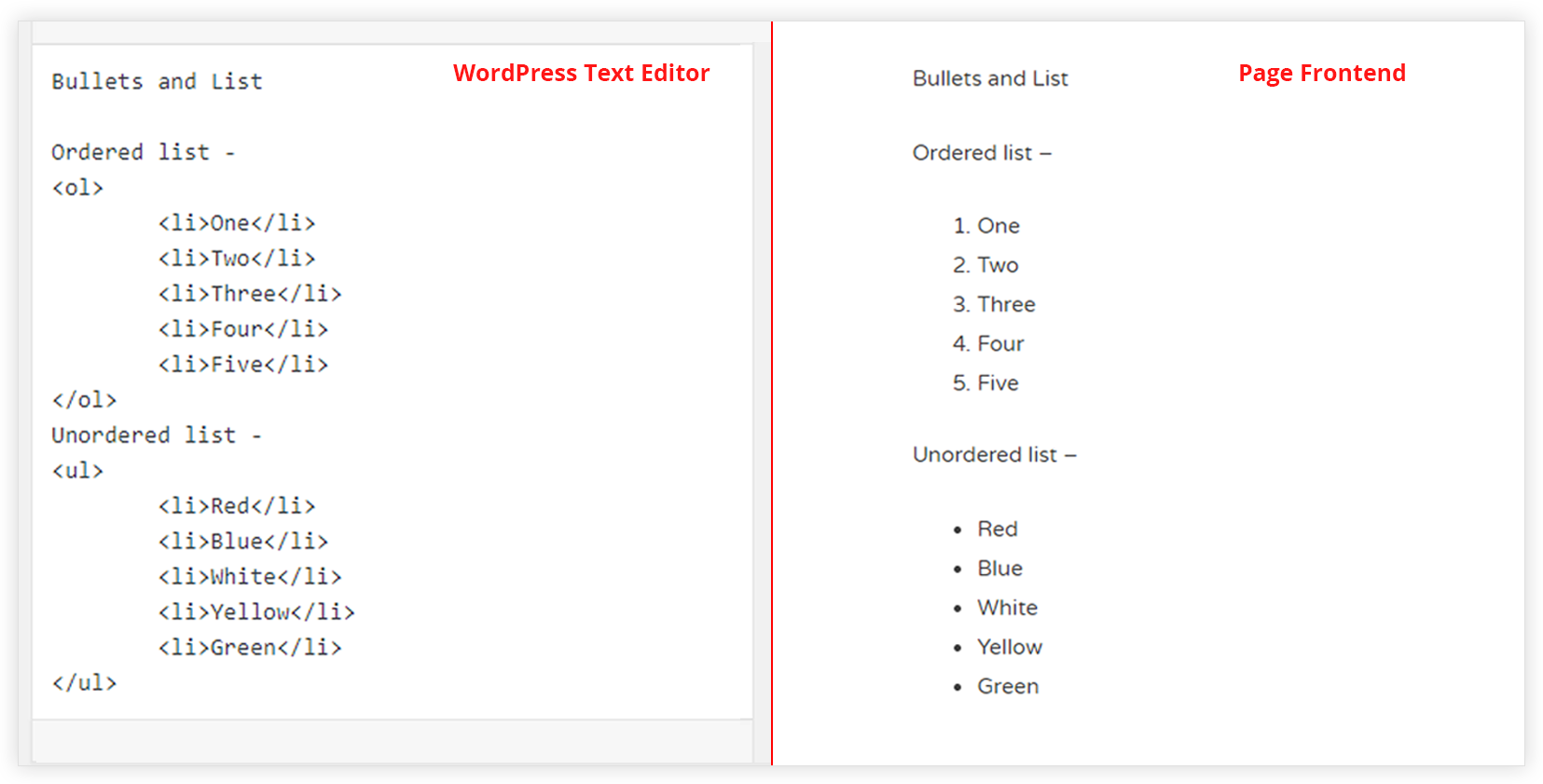
Lists in HTML ::
- HTML offers authors several mechanisms for specifying lists of information. All lists must contain one or more list elements. Lists may contain:
- Unordered information.
- Ordered information.
- Definitions.
-for example, is an unordered list, created with the UL element:
-
- Unordered information.
- Ordered information.
- Definitions. </UL>
HTML tables
Tables can be a useful way of organising content on a web page, particularly text. A table is defined with the <table> tag
- Note
- Each row in the table is defined with the <tr> tag.
- A table heading is defined with the <th> tag.
- Each cell of data in the table is defined with the <td> tag.
## What are web forms?
- Web forms are one of the main points of interaction between a user and a web site or application.

## The <label> Element
- The tag defines a label for many form elements. The element is useful for screen reader users.
- The element also help users who have difficulty clicking on very small regions.
The Submit Button
The <input type=”submit”> defines a button for submitting the form data to a form-handler.
- Example: A form with a submit button: ```
```
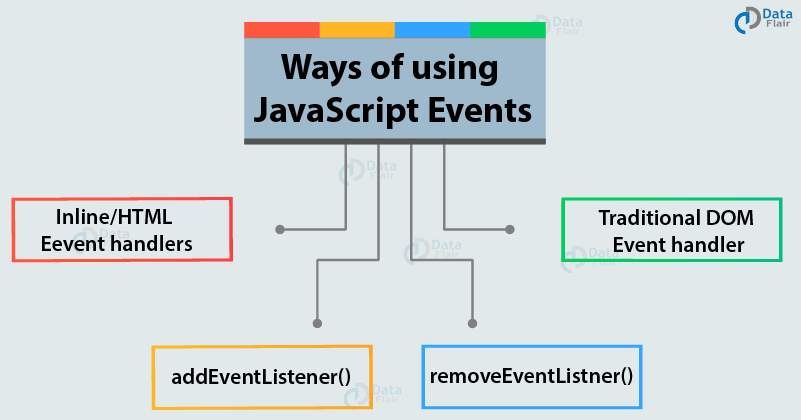
Events
- Events are instances or interactions with the page that trigger code, which responds to the user as a result (example: clicking, tapping, hovering, etc.). When events happen the proper term for that is “fired or been raised” and then they “trigger” a script.
Types of events:
- UI events: User interactions with the browser’s user interface (ex: load, resize and scroll)
- Keyboard events: interactions with keyboards (ex: keypress, up, down)
- Mouse events : interactions using mouse, trackpad or touchscreen (ex: click, hover, double-click )
- Focus event: when an element gains or loses focus
- Form event: when a user interacts with a form
- Mutation evens: when the DOM structure is changed by script
Event flow:
It is important to keep track of order of which events fire. This is known as event flow; the flow can be in either direction
JavaScript HTML DOM EventListener
- The addEventListener() method
- Add an event listener that fires when a user clicks a button:
Events Types:
- Mouse events
- From Netscape 2 onwards all browsers recognize two events on links. When the user moves the mouse into the link area, the mouseover event fires. When he clicks on it the click event fires
- Form events
- Forms recognize the submit and reset events, which — predictably — fire when the user submits or resets a form. The submit event is the key of any form validation script
- interface events
- Interface events are events that are not caused by user actions, but by the result of user actions. When the user clicks on any element he always causes a click event. When clicking on the element has special meaning
Creating custom events
Note:
- All events named on this page are recognized by most browsers when they occur on certain HTML elements. This means that the browser looks if any event handling script is registered to the HTML element for this event.